Falls, electrocution, struck-by, and caught-in or -between. They’re known as The Fatal Four – OSHA’s list of the four leading causes of death in the construction industry. Together they account for almost 60% of fatal injuries, with falls accounting for almost double the next three put together.
Understanding the statistics around falls in the construction industry is crucial for developing effective safety measures and preventing these all-too-common and preventable deaths. Below you will find ten striking statistics related to falls, which will hopefully shedding light on why fall prevention should be a top priority for construction safety managers and business owners alike.
Statistics on Falls in the Construction Industry
Let’s explore some of the conditions, causes, and costs of this all-too-common and preventable cause of deaths in the construction industry:
1. 35% of all construction deaths are caused by falls (1)
2. 1 in 3 falls are from roofs (2)
3. Businesses with 1-10 workers account for more than 70% of fatal falls (1)
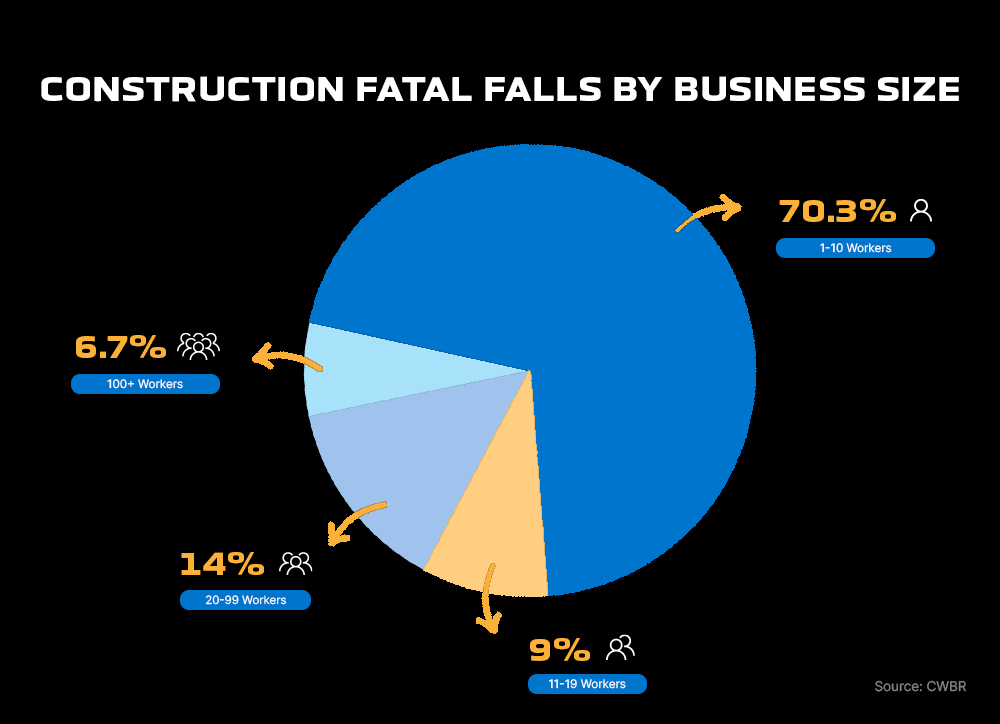
High Risk: Exposure, PPE, and Inspections
4. 62.2% of construction laborers are exposed to heights of more than 5-feet where there are no walls or railings to prevent a fall.(3)
5. Only 31% of construction laborers exposed to heights use PPE (safety harnesses, tethers, etc.)(3)
6. The most cited/inspected/penalized OSHA standard is “Duty to Have Fall Protection” with 6,637 citations and 6,508 inspections in 2022/2023. (4)
7. Four of the top 10 most common OSHA violations are related to working at heights (fall protection, ladders, scaffolding, and fall protection training). (6)
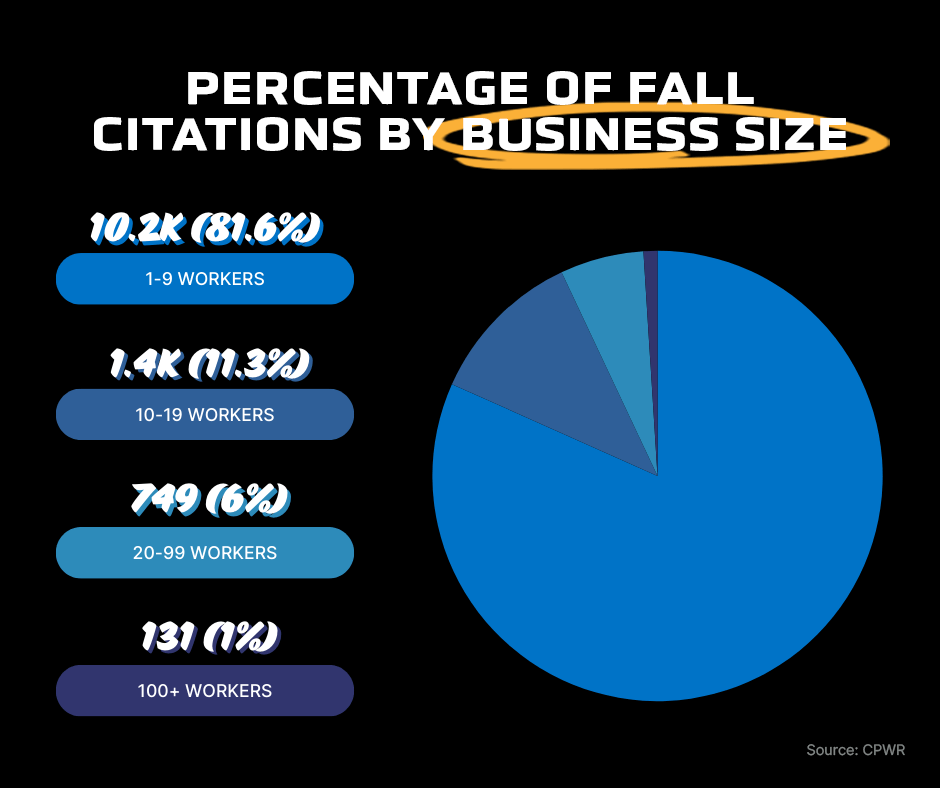
The Cost of Construction-related Falls
8. Businesses that violated the OSHA standard “Duty to Have Fall Protection” paid $47,691,067 in penalties in 2022/2023.(4)
9. Falls to lower levels cost the US construction industry $3.22B in non-fatal worker’s compensation and account for more than 28% of the claims. (7)
10. Falls on the same level cost the US construction industry $1.00B in non-fatal worker’s compensation and account for almost 9% of the claims. (7)
The Importance of Safety Measures to Prevent Falls in Construction
Falls remain the leading cause of death in the construction industry, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive safety measures and adherence to OSHA regulations. By understanding the alarming statistics related to construction falls, construction managers, safety directors, and business owners can take proactive steps to mitigate risks and protect their workers.
Implementing proper fall protection systems, ensuring the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and conducting regular safety inspections are critical strategies for reducing fall-related injuries and fatalities. The substantial financial costs associated with fall-related workers’ compensation claims and OSHA penalties further underscore the importance of investing in robust fall prevention programs. Creating a safer work environment not only saves lives but also enhances productivity and reduces financial liabilities.
Actionable Tips and Best Practices
By implementing effective fall prevention strategies, construction sites can significantly reduce the risk of fall-related injuries and fatalities. Here are some essential tips and best practices to help prevent the most common falls on the jobsite:
Proper Ladder Usage
Ladders are a common tool on construction sites, but improper use can lead to serious falls. Follow these best practices to ensure safe ladder use:
- Three Points of Contact: Always maintain three points of contact (two hands and one foot, or two feet and one hand) when climbing a ladder.
- Stable Surfaces: Set up ladders on stable, level surfaces to prevent tipping. Avoid placing ladders on slippery or uneven ground.
- Proper Angle: Position the ladder at the correct angle (4:1 ratio) to ensure stability. The base of the ladder should be one foot away from the wall for every four feet of ladder height.
- Secure Placement: Ensure the ladder is fully extended and locked before use. Secure the ladder at the top and bottom to prevent movement.
Scaffold Safety
Scaffolds provide essential support for workers at heights, but improper setup and use can lead to falls. Implement these best practices for scaffold safety:
- Proper Erection: Ensure scaffolds are erected and dismantled by trained personnel following manufacturer guidelines.
- Guardrails and Toeboards: Use guardrails and toeboards on all open sides and ends of scaffolds to prevent falls and falling objects.
- Platform Stability: Ensure scaffold platforms are fully planked and stable. Avoid using makeshift platforms or overloading scaffolds.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct daily inspections of scaffolds to check for damage, stability, and proper setup. Repair any issues immediately.
Harness Fitting and Usage
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as safety harnesses, is crucial for preventing falls. Ensure proper fitting and use with these tips:
- Proper Fit: Ensure each worker’s harness fits properly, with the chest strap positioned mid-chest and the leg straps snug but comfortable.
- Inspection: Inspect harnesses and lanyards before each use for signs of wear, damage, or defects. Replace any damaged equipment immediately.
- Anchor Points: Securely attach harnesses to appropriate anchor points capable of supporting at least 5,000 pounds per worker.
- Training: Provide thorough training on the correct use of fall protection equipment, including how to put on, adjust, and inspect harnesses.
Finally, continuous safety training and drills will help reinforce safe work practices and the development of site-specific safety plans is crucial to mitigate the unique hazards for each construction project.
By prioritizing fall prevention and safety compliance, the construction industry can work towards significantly reducing the number of fatal and non-fatal fall incidents, ultimately fostering a culture of safety and responsibility on every construction site.
Sources
- https://www.cpwr.com/wp-content/uploads/DataBulletin-March2024.pdf
- https://www.cpwr.com/wp-content/uploads/publications/The_6th_Edition_Construction_eChart_Book.pdf
- https://www.bls.gov/spotlight/2022/workplace-injuries-and-job-requirements-for-construction-laborers/home.htm
- https://www.osha.gov/ords/imis/citedstandard.naics?p_esize=&p_state=FEFederal&p_naics=23
- https://www.cpwr.com/research/data-center/data-dashboards/osha-inspections-and-citations-in-construction-dashboard/
- https://www.osha.gov/top10citedstandards
- https://business.libertymutual.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/WSI_1002_2023.pdf
